All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The lupus Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lupus Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lupus and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lupus Hub is an independent medical education platform, supported through a founding grant from AstraZeneca. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lupus content recommended for you
Association between history of vaccination and the development of SLE
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) commonly experience immunosuppression, either as a result of the original disease or treatment for SLE; often leading to an increased risk of infections. In the general population, vaccinations are commonplace as prophylactic measures for infection. However, concerns over a possible link between the development or exacerbation of SLE following vaccination has led to uncertainty over administering vaccines in patients with SLE.
Here, we summarize a meta-analysis by Wang et al.1 published in Arthritis Research & Therapy on the association and risk for the development of SLE following vaccination.
Methods1
- A systematic literature search was performed for cohort or case-control studies from inception to September 3, 2023.
- The incidence and risk for SLE following vaccination was analyzed by vaccination type, geographical region, and overall incidence in the total population.
- The adjusted odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) from each trial were used to analyze the association between history of vaccination and risk of SLE.
Key findings1
- A total of 17 studies, comprising 45,067,349 patients who received a vaccination, were included in this meta-analysis.
- Follow-up periods ranged from 0.5 to 2 years post-vaccination.
- In the pooled population, a history of vaccination was not found to be significantly associated with increased risk of SLE (p = 0.348) (Figure 1).
- In a subgroup analysis by vaccination type:
- hepatitis B was the sole vaccination found to be significantly associated with increased risk of SLE;
- the human papillomavirus vaccination also showed a slight increase in OR, but this difference was not significant; and
- the COVID-19 vaccination was associated with a slightly decreased risk of SLE; however, also not significant.
Figure 1. Odds ratio for SLE by history of vaccination*
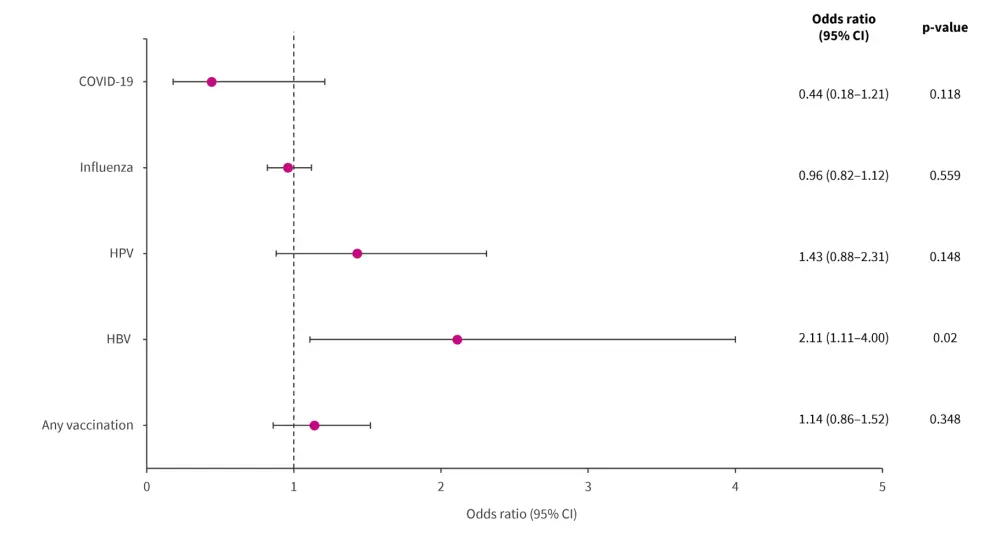
CI, confidence interval; HBV, hepatitis B; HPV, human papillomavirus.
*Data from Wang, et al.1
- In a subgroup analysis by geographical region, a history of vaccination was marginally associated with the risk of SLE in the following regions:
- North America: OR, 1.87 (95% CI, 0.99–3.52; p = 0.053)
- Europe: OR, 0.96 (95% CI, 0.84–1.10; p = 0.551)
- Asia: OR, 0.79 (95% CI, 0.30–2.07; p = 0.628)
- None of the significant associations identified in the individual studies or by subgroup analysis reversed the pooled effect of no association between vaccination and the development of SLE.
|
Key learnings |
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content



