All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The lupus Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lupus Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lupus and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lupus Hub is an independent medical education platform, supported through a founding grant from AstraZeneca. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lupus content recommended for you
Benefit vs risk for COVID-19 vaccination in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) vaccine significantly decreases the risk of infection and COVID-19 clinical events in the general population. However, there is ambiguity surrounding the risk-benefit balance of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with SLE.
Kikuchi et al.1 recently published an article in Immunological Medicine, assessing the effects of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination, including disease flare rates, neutralizing antibody titers, adverse reactions, and associated factors, in patients with SLE. Here, we summarize their findings.
Methods1
- The study enrolled uninfected patients with SLE who received two doses of vaccines (BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273) and historically unvaccinated patients, matched by age and SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI).
- Following the second vaccination adverse reactions, and disease flares were evaluated via clinical assessment, and serum samples were collected to measure neutralizing antibodies.
Key findings1
- The study involved 90 uninfected vaccine-administered patients and 90 unvaccinated control patients.
Seroconversions and adverse reactions
- Within 3 days of the second dose, 88.9% of patients experienced adverse reactions, with 73.6% having local reactions (72.2% with local pain), and 79.2% experiencing systemic reactions.
- Neutralizing antibodies were measured at a mean of 27.6 days post-second dose, where 21.1% of patients tested negative.
- Predictors of non-seroconversion:
- as per univariate analysis were age, longer disease duration, anemia with hemoglobin ≤11 mg/dL, hydroxychloroquine use, mycophenolate mofetil use, and a lower percentage of fever as an adverse reaction; and
- as per multivariate logistic regression analysis were anemia and mycophenolate mofetil use.
Disease activity and flares of SLE
- The SLEDAI increased modestly but significantly after the second dose of vaccination (p = 0.016).
- After ≥8 days post-second dose, 14.4% of patients experienced flares, with 4.4% experiencing severe flares (nephritis in three cases and vasculitis in one). On average, the flares occurred 35 days after the second dose of the vaccine.
- Predictors of flares:
- as per univariate analysis were high titers of SLEDAI, anti-dsDNA antibodies, rash, and azathioprine use before the first dose of the vaccine; and
- as per multivariate logistic regression analysis were high levels of SLEDAI and anti-dsDNA antibodies.
- Flares were not associated with hydroxychloroquine use, neutralizing antibody titers, vaccine type, and adverse reactions or flares in the year before the first dose of vaccine.
Comparison of vaccine-administered patients vs historical unvaccinated controls
- The vaccine-administered patients experienced significantly higher flare incidence and slightly increased SLEDAI, compared with unvaccinated controls (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Comparison in A flares, B disease activity, and C–E serological parameters between the vaccine-administered patients with SLE and the unvaccinated controls*
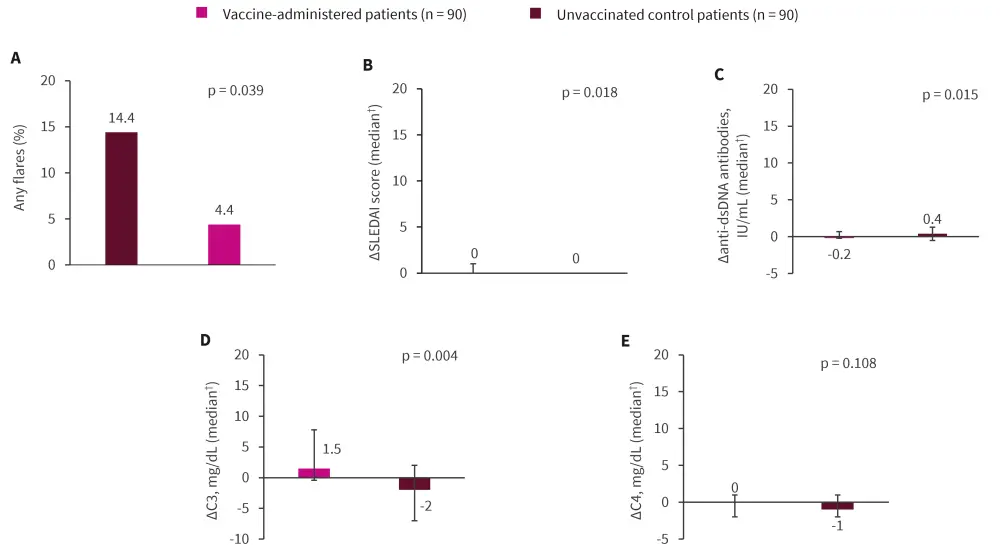
dsDNA, double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid; SLEDAI, SLE Disease Activity Index.
*Data from Kikuchi, et al.1
†Error bars represent the interquartile range; change (∆) was calculated by subtracting the baseline visit from the subsequent visit.
Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
|
Key learnings |
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content


