All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional.
The lupus Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lupus Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lupus and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lupus Hub is an independent medical education platform, supported through a founding grant from AstraZeneca. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lupus content recommended for you
Belimumab for the treatment of refractory lupus nephritis: Real-word experience from three clinical cases
Belimumab is a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved treatment for patients aged ≥5 years with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or lupus nephritis (LN) who are receiving standard therapy.1 Approval in LN was based on the positive results from the BLISS-LN trial, previously reported on the Lupus Hub, which examined belimumab alongside standard-of-care therapy (glucocorticoids, with mycophenolate mofetil or cyclophosphamide-azathioprine) in patients with class III/IV/V LN. The trial did not include patients for whom conventional therapies failed to yield a response.2
Below, we summarize a case series accessing efficacy and safety of belimumab in three patients with refractory LN, published by Malaweera et al. in Internal Medical Journal.2
Study design2
A retrospective review of longitudinal data included in the Australian Lupus Registry and Biobank (ALRB) between 2010 and 2021 for three identified patients treated with belimumab for refractory LN. With their informed consent, baseline demographic and clinical information was obtained. Belimumab (10 mg/kg) was administered intravenously on Days 0, 14, 38, and monthly thereafter.
Key findings
An overview of the three patient cases is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Clinical case overviews for A Case 1, B Case 2, and C Case 3*
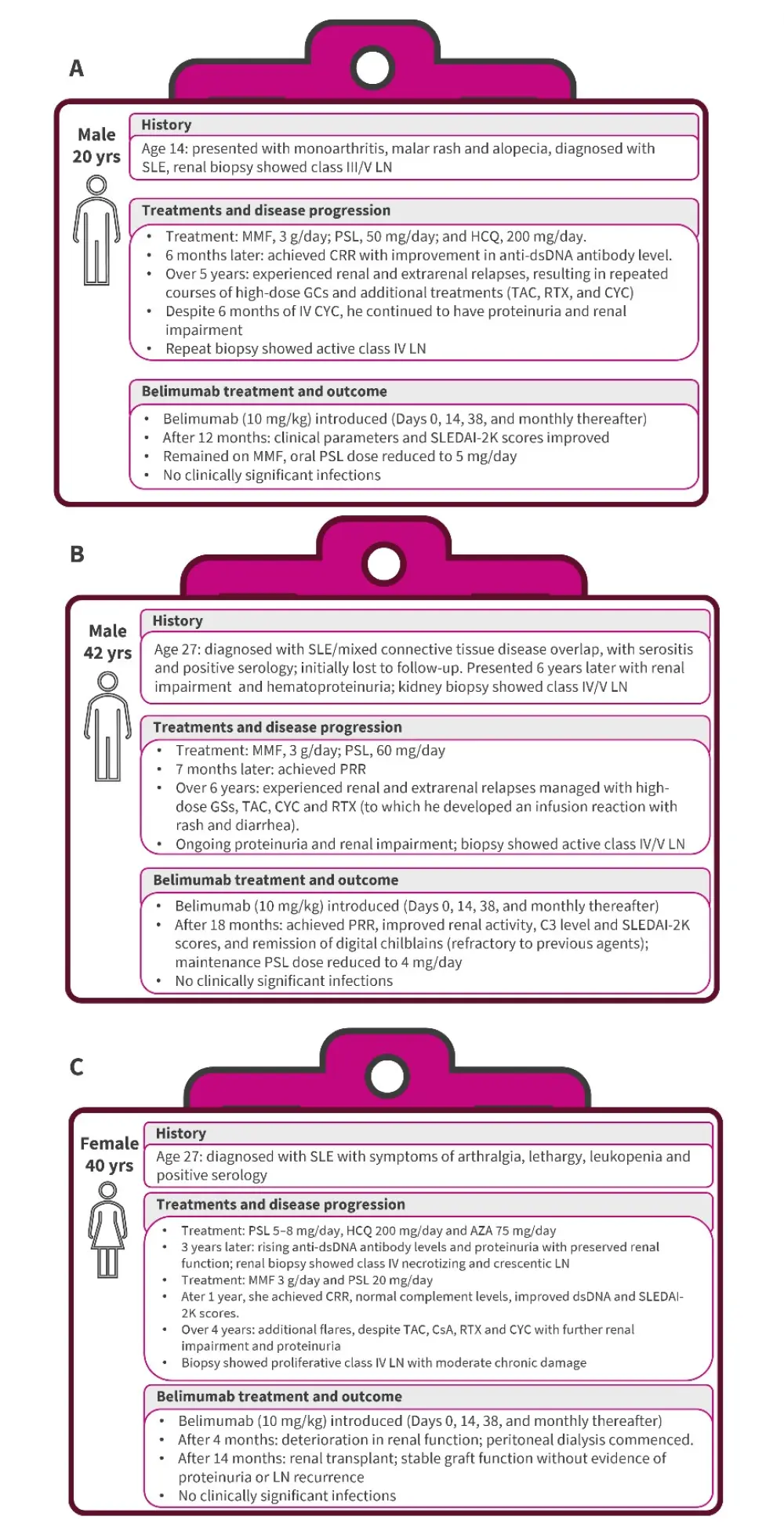
AZA, azathioprine; CRR, complete renal response; CsA, cyclosporine; CTC, cyclophosphamide; CYC, cyclophosphamide; ds, double stranded; GC, glucocorticoid; HCQ, hydroxychloroquine; LN, lupus nephritis; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; PRR, partial renal response; PSL, prednisolone; RTX, rituximab; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; TAC, tacrolimus.
*Data from Malaweera, et al.1
| Key learnings |
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content

